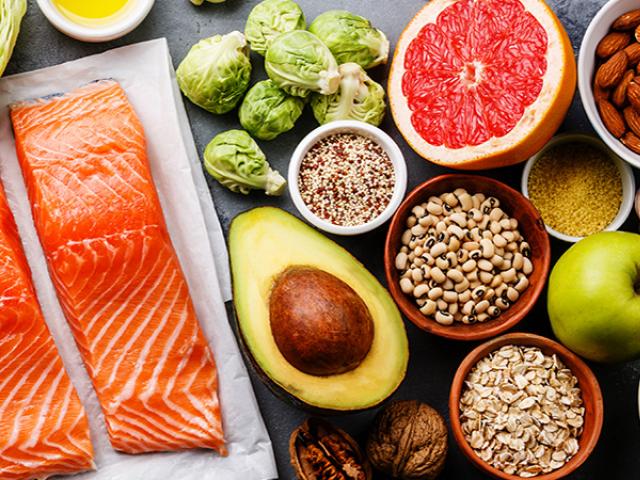
In the realm of nutrition and wellness, few topics have garnered as much attention and acclaim as Omega-3 fatty acids. These essential nutrients, commonly found in Fish oil like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, have been lauded for their myriad health benefits, particularly concerning heart health. But what does the research say about Omega-3 and its impact on cardiovascular well-being? Let’s delve into the science to uncover the truth behind this nutritional powerhouse.
Understanding Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Before we dissect the relationship between Omega-3 and heart health, it’s crucial to grasp the basics of these fatty acids. Omega-3s belong to a family of polyunsaturated fats, consisting of three primary types: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). While ALA is predominantly found in plant sources like flaxseeds and walnuts, EPA and DHA are primarily sourced from marine sources.
The Heart of the Matter: Omega-3 and Cardiovascular Health
Numerous studies over the years have explored the potential cardiovascular benefits of Omega-3 fatty acids, with compelling findings. One of the most significant ways in which Omega-3 exerts its protective effects on the heart is through its ability to reduce triglyceride levels in the bloodstream. High levels of triglycerides are a known risk factor for heart disease.
Additionally, Omega-3s exhibit anti-inflammatory properties, which can help combat chronic inflammation—a hallmark of many cardiovascular conditions, including atherosclerosis. By reducing inflammation within the arterial walls, Omega-3 fatty acids may contribute to improved endothelial function and reduced risk of plaque formation, thereby promoting overall heart health.
Furthermore, emerging research suggests that Omega-3s may play a role in lowering blood pressure levels, another critical factor in maintaining cardiovascular wellness. By promoting vasodilation and improving arterial elasticity, these fatty acids may help regulate blood pressure and reduce the strain on the heart, potentially lowering the risk of hypertension and related complications.
Navigating the Seas of Research: What Studies Reveal
The body of evidence supporting the cardiovascular benefits of Omega-3 fatty acids is vast and continues to expand with ongoing research. A meta-analysis published in the Journal of the American Heart Association pooled data from multiple randomized controlled trials and found that Omega-3 was associated with a significant reduction in cardiovascular events, including heart attacks and strokes.
Moreover, observational studies have highlighted the positive correlation between higher Omega-3 intake and a lower incidence of cardiovascular disease mortality. These findings underscore the importance of incorporating Omega-3-rich foods into one’s diet.

Practical Recommendations and Considerations
While the research surrounding Omega-3 and heart health is promising, it’s essential to approach medication with caution and consult with a healthcare professional, particularly for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking blood-thinning medications. Furthermore, obtaining Omega-3s from whole food sources is generally recommended.
Incorporating fatty fish into your diet a few times a week can be an excellent way to boost your Omega-3 intake naturally. For those who may struggle to consume sufficient amounts of fish, consider incorporating plant-based sources of Omega-3s, such as chia seeds, and algae-based.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the research surrounding Omega-3 fatty acids and heart health paints a compelling picture of their potential benefits. From reducing triglyceride levels and inflammation to improving endothelial function and blood pressure regulation, Omega-3s offer a multifaceted approach to cardiovascular wellness. By incorporating Omega-3-rich foods into your diet.